Cable Testing
Our cable testing services are designed to ensure the integrity, reliability, and safety of all power and control cables. By detecting insulation weaknesses, moisture ingress, or faults early, we help prevent unexpected downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the operational life of your cable infrastructure. Our comprehensive testing methods cover low, medium, and high-voltage systems to maintain uninterrupted electrical supply.
.jpg)
VLF (Very Low Frequency)
VLF testing applies a very low-frequency AC voltage to evaluate cable insulation strength without causing damage. This method is particularly effective for medium- and high-voltage cables, allowing early detection of insulation deterioration, voids, or partial discharges. By identifying weak sections before failure, VLF testing helps plan timely maintenance and avoids costly unplanned outages.
- Dielectric withstand testing under very low frequency AC
- Detection of partial discharge and insulation defects
- Identification of weakened or deteriorated cable sections
- Analysis for insulation ageing and degradation
- Condition assessment for preventive maintenance planning
- Overcurrent relay calibration
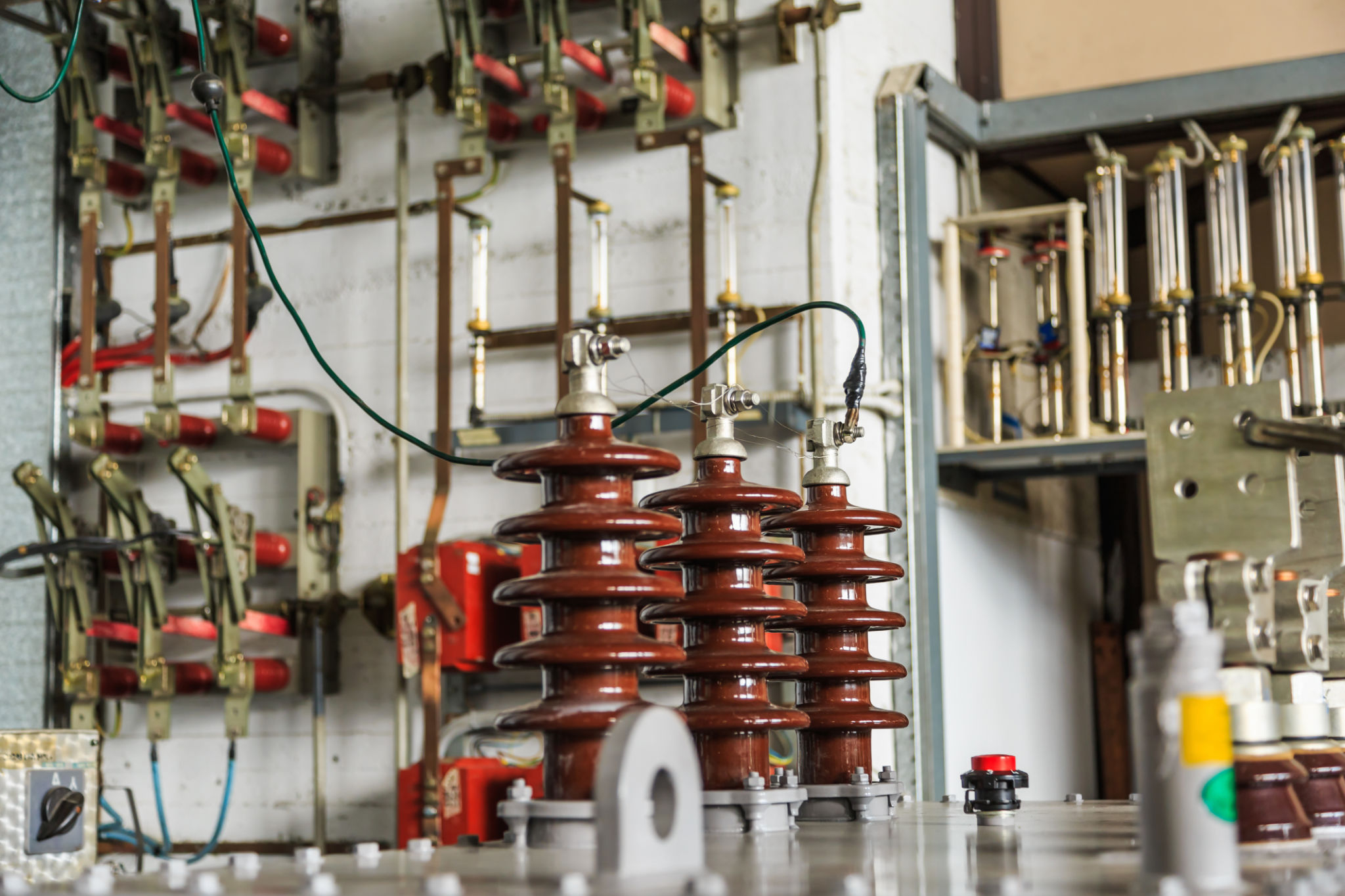
Hipot (High Potential)
Hipot testing subjects cable insulation to a high-voltage AC or DC signal to verify its ability to withstand operational and overvoltage conditions. It is a critical test for ensuring cable safety and reliability, identifying weak points, potential breakdowns, and improper installations before energisation. Hipot testing protects equipment, personnel, and ensures compliance with electrical safety standards.
- High-voltage withstand testing
- Contact erosion measurement
- Vacuum integrity assessment
- Mechanical endurance testing

Cable Fault Analysis
Cable fault analysis helps identify, locate, and assess faults such as open circuits, short circuits, or insulation failures. Accurate fault detection allows targeted repairs and prevents unnecessary downtime. Advanced methods like time-domain reflectometry (TDR) enable precise location mapping for faster maintenance and reduced operational impact.
- Pinpointing of open and short circuits in cable runs
- Analysis of insulation breakdown and degradation
- Use of TDR and other advanced techniques for precise fault location
- Evaluation of cable condition for repair or replacement decisions
- Recommendations for preventive maintenance
- Minimisation of downtime and operational impact
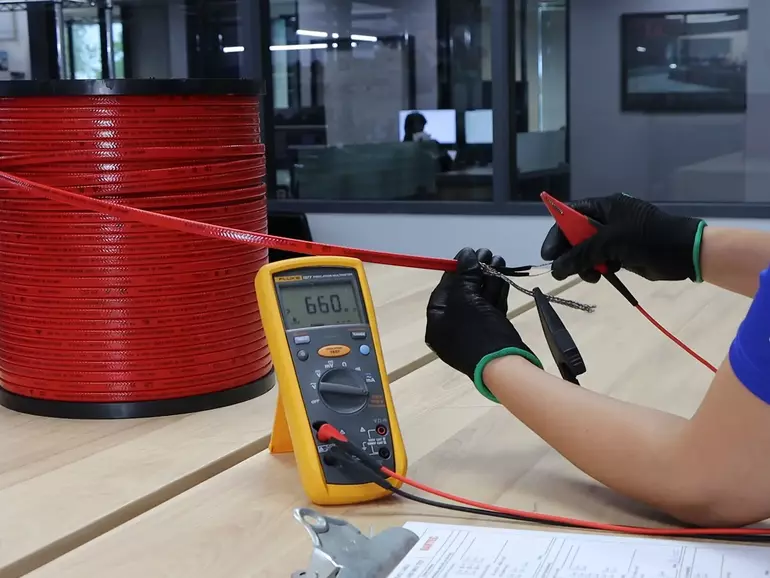

Megger (Insulation Resistance)
Megger testing measures the insulation resistance of cables to evaluate the condition and integrity of their insulation. It helps identify moisture ingress, contamination, or wear and tear before these issues lead to electrical failures. Regular Megger testing ensures long-term safety, reliability, and compliance with industry standards.
- Measurement of insulation resistance at multiple voltage levels
- Detection of moisture, dirt, or insulation damage
- Evaluation of cable health for maintenance planning
- Trend analysis for predicting insulation degradation
- Verification of cable condition before energisation
- Supports preventive maintenance and safety compliance

Tan Delta
Tan Delta testing in cables is a vital method to assess insulation health by measuring dielectric losses. It helps identify moisture ingress, insulation aging, and deterioration in power cables. Regular Tan Delta testing ensures early fault detection, prevents unexpected breakdowns, improves reliability, and extends the service life of critical cable networks.
- Measures dielectric losses in power cables
- Detects moisture ingress and insulation aging
- Identifies early signs of cable deterioration
- Prevents unexpected power outages and failures
- Extends service life of cable networks
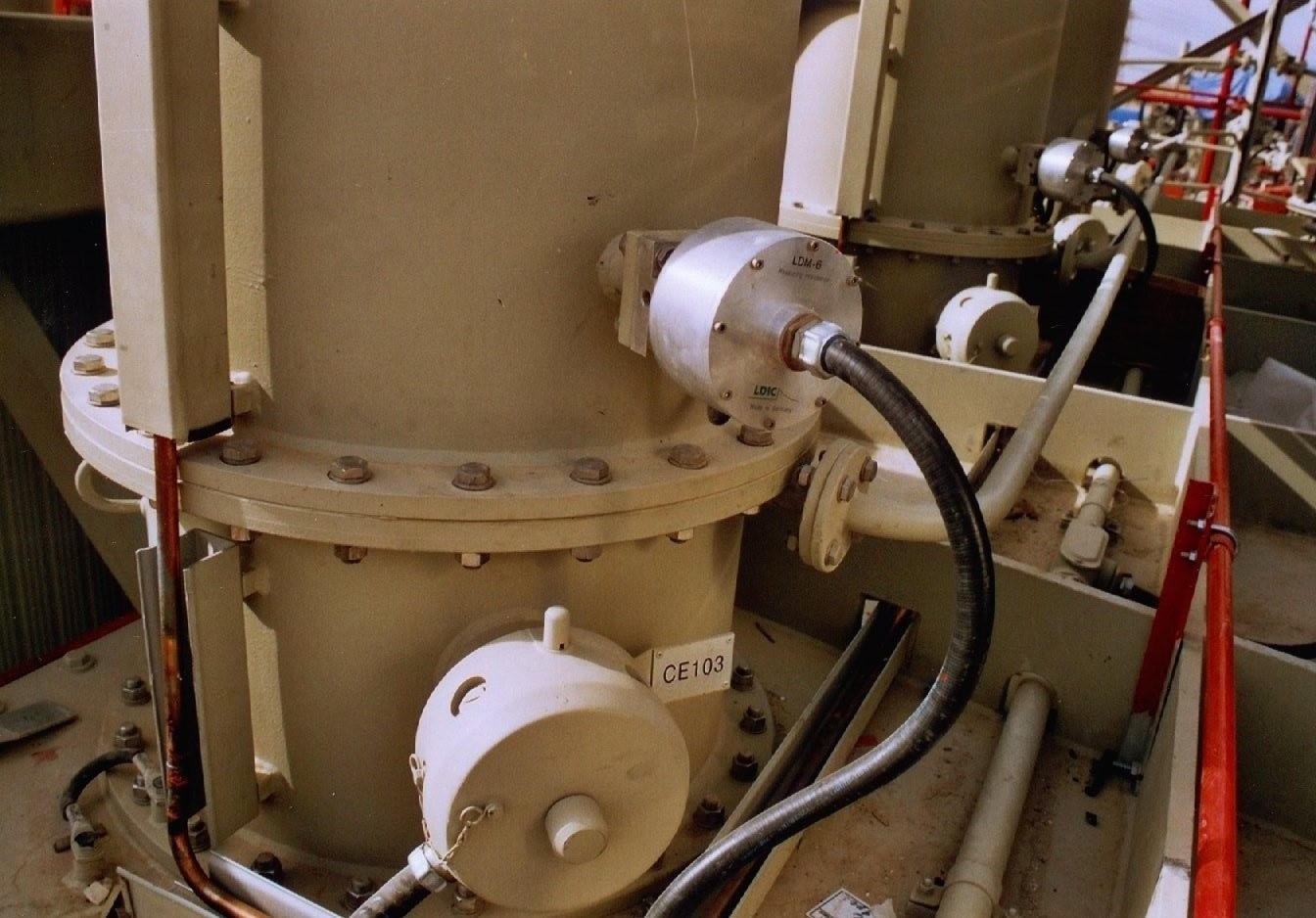
PD (Partial Discharge)
Partial Discharge (PD) testing is a crucial diagnostic technique to assess insulation condition in transformers, switchgear, and cables. It identifies localized electrical discharges caused by insulation defects, voids, or aging. Early detection of PD prevents major insulation failures, enhances equipment reliability, reduces downtime, and ensures safe, long-term operation of power systems.
- Identifies voids, cracks, and aging issues
- Prevents major insulation breakdown failures
- Improves transformer and switchgear reliability
- Supports predictive maintenance and early detection
- Ensures safe and long-term equipment operation