Motor Testing
Our motor testing services ensure optimal performance, detect faults early, and extend the service life of your equipment. We perform various specialised tests to assess the electrical and mechanical health of motors.

MCSA (Motor Current Signature Analysis)
Motor Current Signature Analysis (MCSA) is a reliable diagnostic technique to detect faults in motors and transformers. It identifies electrical and mechanical issues like rotor bar damage, bearing faults, and eccentricity. MCSA ensures early fault detection, reduces downtime, and enhances equipment reliability, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operation
- Detects early faults in motor systems
- Ensures reliable and continuous operation
- Identifies electrical and mechanical abnormalities
- Reduces downtime with predictive diagnostics
- Enhances motor performance and efficiency
- Improves equipment life with fault detection
PD (Partial Discharge)
Partial discharge testing detects small electrical sparks within motor windings or insulation systems, which are often invisible to the naked eye but can lead to significant damage over time. By identifying these discharges early, we can pinpoint weak spots in the insulation and recommend corrective actions before a major failure occurs, ensuring motors remain reliable under demanding operational loads.
- Detection of insulation breakdown points
- Measurement of discharge levels and patterns
- Location pinpointing of discharge sites
- Trend monitoring for progressive deterioration
- Recommendations for rewinding or insulation replacement

Tan Delta
Tan Delta testing measures dielectric losses in motor insulation to evaluate its health and predict remaining service life. A rise in Tan Delta values indicates possible moisture ingress, contamination, or insulation ageing. This test is especially useful for high-voltage motors where insulation breakdown can result in costly downtime and repairs.
- Measurement of insulation loss factors
- Identification of moisture or contamination issues
- Voltage-dependent dissipation factor measurement
- Comparative analysis with historical test data
- Predictive maintenance recommendations

RLA (Rated / Running Load Amps)
Rated/Running Load Amps (RLA) testing is vital for assessing transformer and motor performance under actual load conditions. It verifies that current draw remains within safe limits, preventing overheating, insulation damage, and energy losses. RLA ensures efficiency, reliability, and long-term operational safety of electrical equipment in service.
- Measurement of running load current under normal operation
- Comparison against manufacturer-rated RLA
- Identification of overload conditions
- Detection of phase imbalance or poor power factor
- Recommendations for load balancing or mechanical inspection
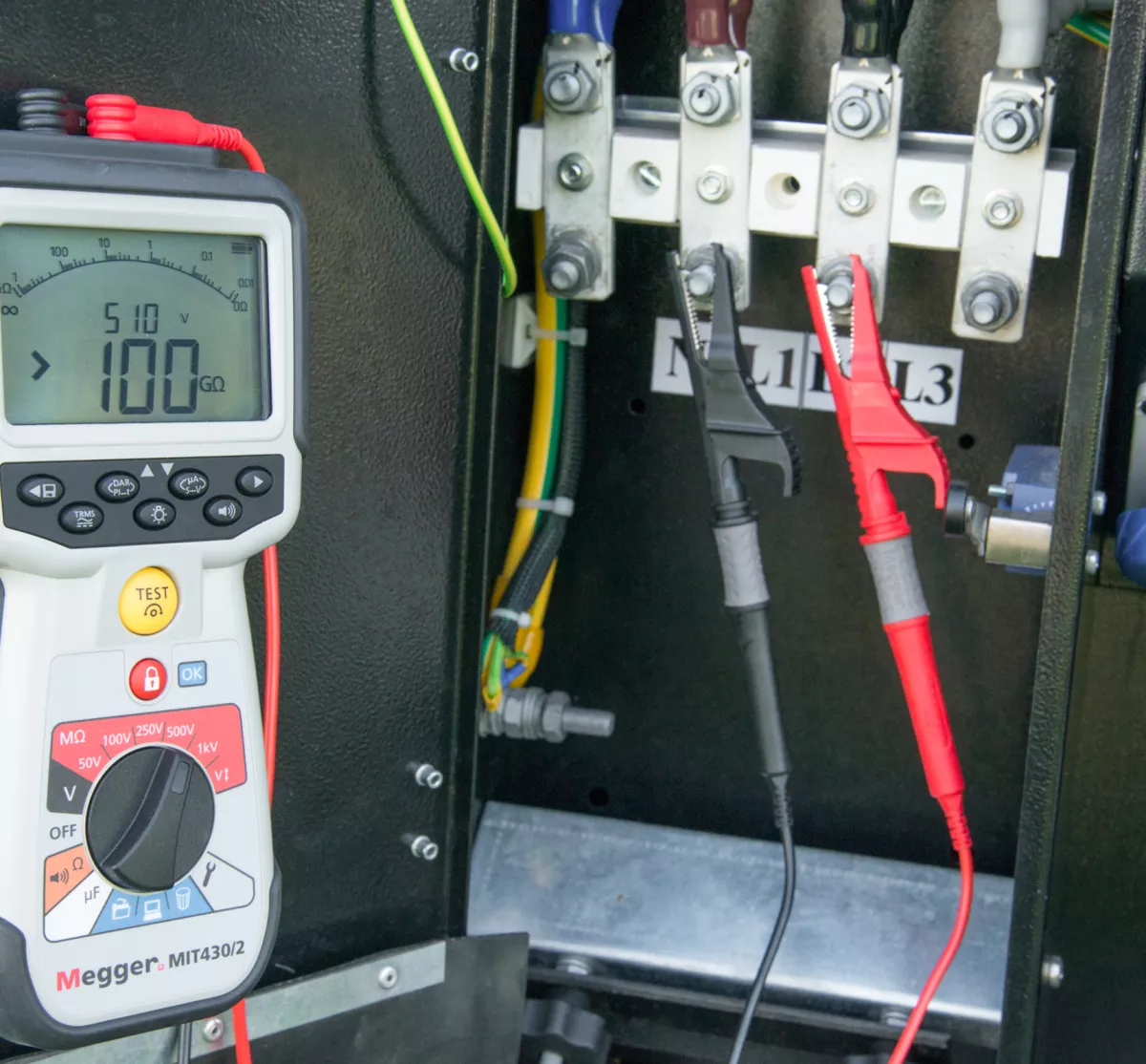
IR (Insulation resistance)
Insulation Resistance (IR) testing is a fundamental diagnostic method to evaluate the quality of electrical insulation in transformers, motors, and cables. It detects moisture, dirt, and insulation deterioration that may lead to faults. IR measurement ensures safety, prevents breakdowns, and enhances reliability of electrical equipment in operation.
- Detects moisture and insulation deterioration early
- Ensures electrical equipment safety and reliability
- Prevents short circuits and costly breakdowns
- Evaluates insulation quality under test conditions
- Identifies faults before major system failure